Amedeo Clemente Modigliani (
July 12,
1884 –
January 24,
1920) was an
Italian artist, practicing both
painting and
sculpture, who pursued his career for the most part in France. Modigliani was born in
Livorno (historically referred to in English as Leghorn), in
Central Italy and began his artistic studies in Italy before moving to
Paris in 1906. Influenced by the artists in his circle of friends and associates, by a range of
genres and
art movements, and by
primitive art, Modigliani's
œuvre was nonetheless
unique and
idiosyncratic. He died in Paris of
tubercular meningitis— exacerbated by
poverty,
overworking, and an excessive use of
alcohol and
narcotics — at the age of 35.
Early life Modigliani is known to have drawn and painted from a very early age, and thought himself "already a painter", his mother wrote, even before beginning formal studies. Despite her misgivings that launching him on a course of studying art would impinge upon his other studies, his mother indulged the young Modigliani's passion for the subject.
At the age of fourteen, while sick with the typhoid fever, he raved in his delirium that he wanted, above all else, to see the paintings in the
Palazzo Pitti and the
Uffizi in
Florence. As Livorno's local museum only housed a sparse few paintings by the Italian Renaissance masters, the tales he had heard about the great works held in Florence intrigued him, and it was a source of considerable despair to him, in his sickened state, that he might never get the chance to view them in person. His mother promised that she would take him to
Florence herself, the moment he was recovered. Not only did she fulfil this promise, but she also undertook to enrol him with the best painting master in Livorno,
Guglielmo Micheli.
Art student years Modigliani worked in Micheli's Art School from 1898 to 1900. Here his earliest formal artistic instruction took place in an atmosphere deeply steeped in a study of the styles and themes of nineteenth-century Italian art. In his earliest Parisian work, traces of this influence, and that of his studies of
Renaissance art, can still be seen: artists such as
Giovanni Boldini figure just as much in this nascent work as do those of
Toulouse-Lautrec.
Modigliani showed great promise while with Micheli, and only ceased his studies when he was forced to, by the onset of tuberculosis.
In 1901, whilst in Rome, Modigliani admired the work of
Domenico Morelli, a painter of melodramatic Biblical studies and scenes from great literature. It is ironic that he should be so struck by Morelli, as this painter had served as an inspiration for a group of iconoclasts who went by the title, the
Macchiaioli (from
macchia—"dash of colour", or, more derogatively, "stain"), and Modigliani had already been exposed to the influences of the Macchiaioli. This minor, localized art movement was possessed of a need to react against the bourgeois stylings of the academic genre painters. While sympathetically connected to (and actually pre-dating) the
French Impressionists, the Macchiaioli did not make the same impact upon international art culture as did the followers of
Monet, and are today largely forgotten outside of Italy.
Modigliani's connection with the movement was through Guglielmo Micheli, his first art teacher. Micheli was not only a Macchiaioli himself, but had been a pupil of the famous
Giovanni Fattori, a founder of the movement. Micheli's work, however, was so fashionable and the genre so commonplace that the young Modigliani reacted against it, preferring to ignore the obsession with landscape that, as with French Impressionism, characterized the movement. Micheli also tried to encourage his pupils to paint
en plein air, but Modigliani never really got a taste for this style of working, sketching in cafés, but preferring to paint indoors, and especially in his own studio. Even when compelled to paint landscapes (three are known to exist),
In 1902, Modigliani continued what was to be a life-long infatuation with life drawing, enrolling in the
Accademia di Belle Arti (Scuola Libera di Nudo, or "Free School of Nude Studies") in
Florence. A year later while still suffering from tuberculosis, he moved to
Venice, where he registered to study at the
Istituto di Belle Arti.
It is in Venice that he first smoked
hashish and, rather than studying, began to spend time frequenting disreputable parts of the city. The impact of these lifestyle choices upon his developing artistic style is open to conjecture, although these choices do seem to be more than simple
teenage rebellion, or the cliched
hedonism and
bohemianism that was almost expected of artists of the time; his pursuit of the seedier side of life appears to have roots in his appreciation of radical philosophies, such as those of
Nietzsche.
Micheli and the Macchiaioli Having been exposed to erudite philosophical literature as a young boy under the tutelage of Isaco Garsin, his maternal grandfather, he continued to read and be influenced through his art studies by the writings of
Nietzsche,
Baudelaire,
Carducci,
Comte de Lautréamont, and others, and developed the belief that the only route to true creativity was through defiance and disorder.
Letters that he wrote from his 'sabbatical' in Capri in 1901 clearly indicate that he is being more and more influenced by the thinking of Nietzsche. In these letters, he advised friend
Oscar Ghiglia,
The work of
Lautréamont was equally influential at this time. This doomed poet's
Les Chants de Maldoror became the seminal work for the Parisian
Surrealists of Modigliani's generation, and the book became Modigliani's favourite to the extent that he learnt it by heart.
Early literary influences Paris In 1906 Modigliani moved to Paris, then the focal point of the
avant-garde. In fact, his arrival at the epicentre of artistic experimentation coincided with the arrival of two other foreigners who were also to leave their marks upon the art world:
Gino Severini and
Juan Gris.
He settled in
Le Bateau-Lavoir, a
commune for penniless artists in
Montmartre, renting himself a studio in Rue Caulaincourt. Even though this artists' quarter of Montmartre was characterized by generalized poverty, Modigliani himself presented - initially, at least - as one would expect the son of a family trying to maintain the appearances of its lost financial standing to present: his wardrobe was dapper without ostentation, and the studio he rented was appointed in a style appropriate to someone with a finely attuned taste in plush drapery and Renaissance reproductions. He soon made efforts to assume the guise of the bohemian artist, but, even in his brown corduroys, scarlet scarf and large black hat, he continued to appear as if he were slumming it, having fallen upon harder times.
Arrival Within a year of arriving in Paris, however, his demeanour and reputation had changed dramatically. He transformed himself from a dapper academician artist into a sort of prince of vagabonds.
The poet and journalist
Louis Latourette, upon visiting the artist's previously well-appointed studio after his transformation, discovered the place in upheaval, the Renaissance reproductions discarded from the walls, the plush drapes in disarray. Modigliani was already an alcoholic and a drug addict by this time, and his studio reflected this. Modigliani's behaviour at this time sheds some light upon his developing style as an artist, in that the studio had become almost a sacrificial effigy for all that he resented about the academic art that had marked his life and his training up to that point.
Not only did he remove all the trappings of his bourgeois heritage from his studio, but he also set about destroying practically all of his own early work. He explained this extraordinary course of actions to his astonished neighbours thus:
The motivation for this violent rejection of his earlier self is the subject of considerable speculation. The self-destructive tendencies may have stemmed from his tuberculosis and the knowledge (or presumption) that the disease had essentially marked him for an early death; within the artists' quarter, many faced the same sentence, and the typical response was to set about enjoying life while it lasted, principally by indulging in self-destructive actions. For Modigliani such behavior may have been a response to a lack of recognition; it is known that he sought the company of other alcoholic artists such as
Utrillo and
Soutine, seeking acceptance and validation for his work from his colleagues. that it is entirely possible for Modigliani to have achieved even greater artistic heights had he not been immured in, and destroyed by, his own self-indulgences. We can only speculate what he might have accomplished had he emerged intact from his self-destructive explorations.
Transformation During his early years in Paris, Modigliani worked at a furious pace. He was constantly sketching, making as many as a hundred drawings a day. However, many of his works were lost - destroyed by him as inferior, left behind in his frequent changes of address, or given to girlfriends who did not keep them. Tall (Modigliani was only 5 foot 5 inches) with dark hair (like Modigliani's), pale skin and grey-green eyes, she embodied Modigliani's aesthetic ideal and the pair became engrossed in each other. After a year, however, Anna returned to her husband.
Output In 1909, Modigliani returned home to Livorno, sickly and tired from his wild lifestyle. Soon he was back in Paris, this time renting a
studio in
Montparnasse. He originally saw himself as a sculptor rather than a painter, and was encouraged to continue after
Paul Guillaume, an ambitious young art dealer, took an interest in his work and introduced him to sculptor
Constantin Brancusi.
Although a series of Modigliani's sculptures were exhibited in the
Salon d'Automne of 1912, by 1914 he abandoned sculpting and focused solely on his painting, a move precipitated by the difficulty in acquiring stone, and by Modigliani's physical debilitation.
Sculpture In Modigliani's art, there is evidence of the influence of primitive art from
Africa and
Cambodia which he may have seen in the
Musée de l'Homme, but his stylizations are just as likely to have been the result of his being surrounded by Mediæval sculpture during his studies in Northern Italy (there is no recorded information from Modigliani himself, as there is with
Picasso and others, to confirm the contention that he was influenced by either ethnic or any other kind of sculpture). A possible interest in
African tribal masks seems to be evident in his portraits. In both his painting and sculpture, the sitters' faces resemble ancient
Egyptian painting in their flat and mask-like appearance, with distinctive almond eyes, pursed mouths, twisted noses, and elongated necks. However these same characteristics are shared by Mediæval European sculpture and painting.
Modigliani painted a series of portraits of contemporary artists and friends in Montparnasse:
Chaim Soutine,
Moise Kisling,
Pablo Picasso,
Diego Rivera,
Marie "Marevna" Vorobyev-Stebeslka,
Juan Gris,
Max Jacob,
Blaise Cendrars, and
Jean Cocteau, all sat for stylized renditions.
At the outset of
World War I, Modigliani tried to enlist in the
army but was refused because of his poor health.
Question of influences Known as
Modì, which translates as 'cursed' (maudit), by many Parisians, but as
Dedo to his family and friends, Modigliani was a handsome man, and attracted much female attention.
Women came and went until Beatrice Hastings entered his life. She stayed with him for almost two years, was the subject for several of his portraits, including
Madame Pompadour, and the object of much of his drunken wrath.
When the
British painter
Nina Hamnett arrived in Montparnasse in 1914, on her first evening there the smiling man at the next table in the
café introduced himself as
Modigliani; painter and Jew. They became great friends.
In 1916, Modigliani befriended the
Polish poet and art dealer
Leopold Zborovski and his wife Anna.
The war years The following summer, the
Russian sculptor
Chana Orloff introduced him to a beautiful 19-year-old art student named
Jeanne Hébuterne who had posed for
Tsuguharu Foujita. From a conservative
bourgeois background, Hébuterne was renounced by her devout
Roman Catholic family for her liaison with the painter, whom they saw as little more than a debauched derelict, and, worse yet, a Jew. Despite her family's objections, soon they were living together, and although Hébuterne was the love of his life, their public scenes became more renowned than Modigliani's individual drunken exhibitions.
On
December 3,
1917, Modigliani's first one-man
exhibition opened at the Berthe Weill Gallery. The chief of the Paris
police was scandalized by Modigliani's nudes and forced him to close the exhibition within a few hours after its opening.
After he and Hébuterne moved to
Nice, she became pregnant and on
November 29,
1918 gave birth to a daughter whom they named Jeanne (1918-1984).
Jeanne Hébuterne During a trip to Nice, conceived and organized by Leopold Zborovski, Modigliani, Foujita and other artists tried to sell their works to rich
tourists. Modigliani managed to sell a few pictures but only for a few francs each. Despite this, during this time he produced most of the paintings that later became his most popular and valued works.
During his lifetime he sold a number of his works, but never for any great amount of money. What funds he did receive soon vanished for his habits.
In May of 1919 he returned to Paris, where, with Hébuterne and their daughter, he rented an apartment in the rue de la Grande Chaumière. While there, both Jeanne Hébuterne and Amedeo Modigliani painted portraits of each other, and of themselves.
Nice Although he continued to paint, Modigliani's health was deteriorating rapidly, and his alcohol-induced blackouts became more frequent.
In 1920, after not hearing from him for several days, his downstairs neighbor checked on the family and found Modigliani in bed delirious and holding onto Hébuterne who was nearly nine months pregnant. They summoned a doctor, but little could be done because Modigliani was dying of the then-incurable disease
tubercular meningitis.
Modigliani died on January 24,
1920. There was an enormous
funeral, attended by many from the artistic communities in
Montmartre and
Montparnasse.
Hébuterne was taken to her parents' home, where, inconsolable, she threw herself out of a fifth-floor window two days after Modigliani's death, killing herself and her unborn child. Modigliani was interred in
Père Lachaise Cemetery. Hébuterne was buried at the
Cimetière de Bagneux near Paris, and it was not until 1930 that her embittered family allowed her body to be moved to rest beside Modigliani.
Modigliani died penniless and destitute—managing only one solo exhibition in his life and giving his work away in exchange for meals in restaurants. Had he lived through the
1920s when American buyers flooded
Paris, his fortunes might well have changed. Since his death his reputation has soared. Nine novels, a play, a documentary and three feature films have been devoted to his life.
Death Painting the Century 101 Portrait Masterpieces 1900-2000  Selected paintings
Selected paintings (Only 27 sculptures by Modigliani are known to exist.)
Head of a Woman (1910/1911).
Head (1911-1913).
Head (1911-1912).
Head (1912).
Rose Caryatid (1914).

 Television Show Collections
Television Show Collections H.261 design
H.261 design
 Diocese
Diocese In
In  cannot represent the mass of any rotating or charged body.
cannot represent the mass of any rotating or charged body.  Important things to stress
Important things to stress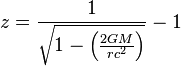 , where
, where is the
is the  is the
is the  is the radial coordinate of the observer (which is analogous to the classical distance from the center of the object, but is actually a
is the radial coordinate of the observer (which is analogous to the classical distance from the center of the object, but is actually a  is the
is the  Selected paintings
Selected paintings Coverage
Coverage


 Lefthit
Lefthit